Wildlife Biology
Wildlife biology is an enchanting area that delves into the intricate methods animals work together with their environments. By finding out animal habits, researchers can uncover the underlying patterns of survival, copy, and social interplay. Understanding these dynamics is essential not just for preserving biodiversity but in addition for managing and defending the habitats these species name dwelling. On this article, we’ll discover the foundational parts of wildlife biology, study the behaviors of varied animal species, and talk about the implications for conservation efforts.
What’s Wildlife Biology?
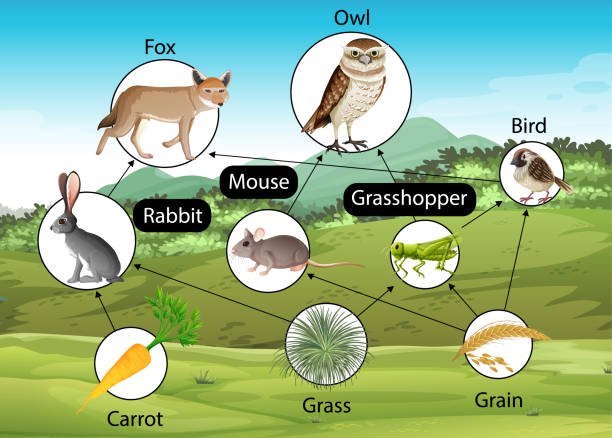
Wildlife biology is a department of ecology that focuses on the research of animals of their pure habitats. It encompasses a wide range of disciplines, together with zoology, ecology, and environmental science. Wildlife biologists typically have interaction in area research, analysis initiatives, and conservation initiatives to know species interactions, migration patterns, reproductive behaviors, and the impacts of environmental modifications on wildlife.
Key Parts of Wildlife Biology
-
- Animal Habits: Understanding how animals work together with each other and their atmosphere.
-
- Habitat Conservation: Defending and preserving the areas numerous species inhabit.
-
- Inhabitants Dynamics: Learning the inhabitants sizes and constructions of various species and the way they modify over time.
-
- Ecological Relationships: Investigating how totally different species coexist and compete inside ecosystems.
The Significance of Learning Animal Habits
Understanding animal habits is pivotal in wildlife biology. Completely different species exhibit distinctive diversifications to thriving in numerous habitats, whether or not it is the stealthy looking methods of a predator or the advanced social constructions of sure primates. By monitoring these behaviors, researchers can achieve insights into:
-
- Survival Methods: Investigating how animals discover meals, keep away from predators, and adapt to altering environments.
-
- Reproductive Patterns: Observing mating rituals, parenting methods, and social bonding amongst animals.
-
- Social Constructions: Analyzing how animals talk and type relationships inside their teams.
Behavioral Insights from Varied Species
1. Carnivores: The Carnivorous Hunter
Carnivores, akin to wolves and lions, are sometimes seen as apex predators. Understanding their looking habits can make clear their position in sustaining ecosystem steadiness.
-
- Pack Dynamics: Wolves, for example, hunt in packs that show intricate social hierarchies. Observing their cooperative methods informs wildlife biology in regards to the significance of social bonds in looking success and territory safety.
-
- Territory Marking: Each wolves and lions set up territories by way of scent marking and vocalizations, which prevents conflicts and promotes useful resource allocation amongst teams.
2. Herbivores: The Grazing Neighborhood
Herbivores, like deer and elephants, exhibit distinctive foraging behaviors and social constructions which can be essential for understanding habitat use.
-
- Migration Patterns: Many herbivores take part in seasonal migrations, pushed by meals availability and local weather modifications. Analyzing these patterns gives insights into how environmental elements affect wildlife actions.
-
- Flocking Habits: Social species, akin to wildebeests, depend on group foraging, lowering predation dangers whereas enabling particular person animals to learn from collective vigilance.
3. Omnivores: Adaptable Survivors
Omnivores, exemplified by bears and raccoons, showcase unimaginable adaptability to varied environmental situations.
-
- Useful resource Utilization: An understanding of their habits reveals how they exploit a number of meals sources, contributing to ecosystem range. Raccoons are recognized for his or her opportunistic foraging, adapting to city environments by exploiting human waste and unprotected meals.
-
- Behavioral Flexibility: This adaptability makes omnivores resilient to habitat modifications, highlighting the necessity for cautious monitoring and administration of their populations.
The Position of Habitats in Shaping Habits
Habitats are excess of simply bodily areas; they form behavioral traits and survival methods of animals. Completely different environments—be it forests, grasslands, or wetlands—compel species to adapt their behaviors in distinctive methods.
1. Terrestrial Habitats
In terrestrial ecosystems, elements akin to vegetation kind, local weather, and human actions considerably affect wildlife habits. For instance, animals in forested areas might develop camouflage and arboreal expertise to evade predators, whereas these dwelling in open grasslands would possibly depend on velocity and agility.
2. Aquatic Habitats
Aquatic environments current distinct challenges, from water currents to variability in meals availability. Fish, for example, exhibit differing mating behaviors primarily based on habitat situations, akin to nesting preferences influenced by water temperature and substrate availability.
3. City Habitats
As cities broaden, understanding wildlife habits in city settings turns into more and more necessary. Animals akin to pigeons, foxes, and raccoons have tailored to life in city environments, showcasing outstanding behavioral flexibility.
Conservation Implications of Wildlife Biology
The insights garnered from understanding animal habits and habitats play a significant position in conservation efforts. Listed here are some actionable insights:
1. Habitat Restoration
Efficient habitat restoration requires a deep understanding of the precise wants of wildlife species. By finding out animal habits, biologists can determine crucial sources and corridors wanted for his or her survival.
2. Implementing Protected Areas
Creating protected areas helps be sure that species can thrive of their pure environments. Habits research can present information on territorial ranges, guaranteeing these zones cowl important habitats.
3. Educating the Public
Elevating consciousness in regards to the significance of animal habits in conservation efforts engages communities. Education schemes can foster respect for native wildlife, encouraging individuals to take part in preservation initiatives.
Conclusion
Wildlife biology serves as a vital lens by way of which we are able to perceive animal habits and its implications for habitats. By finding out the intricate patterns of habits throughout varied species, we not solely illuminate the marvels of nature but in addition pave the best way for efficient conservation methods.
Take Motion!
-
- Get Concerned: Take part in native conservation efforts, whether or not by way of volunteering or advocacy.
-
- Keep Knowledgeable: Comply with wildlife biology analysis and have interaction with organizations working for biodiversity.
-
- Educate Others: Share your data in regards to the significance of wildlife habits and the ecosystems that help it.
In an period the place habitat loss and local weather change threaten innumerable species, leveraging the data from wildlife biology to foster understanding and motion is extra crucial than ever. Let’s unite efforts to make sure a sustainable future for our planet’s wildlife.







